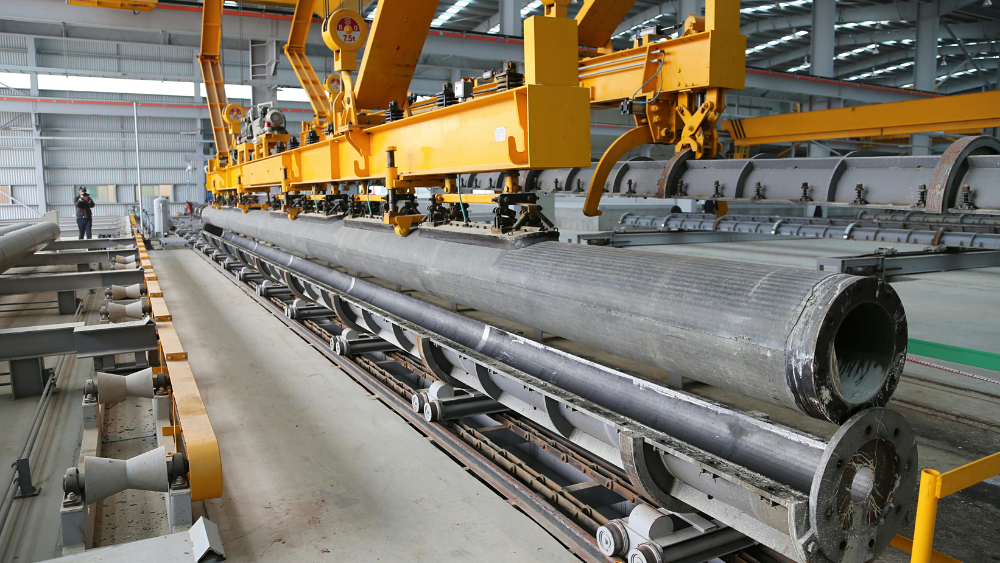
In the world of industrial steel, not all pipes are created equal. Cold-drawn seamless pipes stand out for their exceptional precision, smooth surface finish, and superior strength, making them the go-to choice for applications where accuracy and durability are non-negotiable.
But what exactly makes a cold-drawn seamless pipe different from other types of steel pipes? How does the manufacturing process impact its performance, and why is heat treatment so crucial to ensure stability under high pressure or extreme conditions?
In this complete 2026 guide, we’ll break down the key characteristics, manufacturing techniques, specifications, and applications of cold-drawn seamless pipes. Whether you’re an engineer, procurement professional, or industry enthusiast, this guide will help you understand the value of choosing the right pipe for your project and make informed decisions with confidence.
A cold-drawn seamless pipe (CDS pipe) is a type of seamless steel pipe manufactured through a process called cold drawing. Unlike welded pipes, which are made by rolling and welding steel strips, seamless pipes have no weld seam, which makes them stronger, more precise, and better suited for demanding industrial applications.
The term cold-drawn refers to how the pipe is formed: a hot-rolled seamless pipe is drawn at room temperature through a die (a tool that shapes the steel) to reduce its diameter and wall thickness. This cold working process not only improves the pipe's dimensional accuracy but also enhances its mechanical properties, such as strength, hardness, and surface finish.
Because of these qualities, cold-drawn seamless steel pipes are widely used in industries like oil & gas, automotive, construction, power generation, hydraulics, and mechanical engineering.
When engineers and buyers talk about cold-drawn seamless (CDS) pipes, they're usually referring to a product known for its precision, strength, and reliability. Unlike hot-rolled or welded pipes, CDS pipes undergo an additional cold drawing process that gives them a unique set of characteristics highly valued in critical applications.
Here are the key characteristics that define cold-drawn seamless steel pipes:
Cold drawing allows manufacturers to control outer diameter, inner diameter, and wall thickness with exceptional precision. This means parts fit together more easily in assemblies — a big advantage in automotive, aerospace, and hydraulic systems, where tolerances are tight.
The cold drawing process produces a smooth internal and external surface. A smoother finish reduces friction, improves fluid flow, and makes pipes easier to coat, plate, or paint.
By refining the steel's grain structure, cold drawing improves:
Because these pipes are seamless (no welds), they have consistent strength along the entire length. This minimizes the risk of weak points, cracks, or leaks — critical in industries like oil & gas pipelines, boilers, and power generation.
CDS pipes can be manufactured in a wide range of diameters and wall thicknesses, making them adaptable for everything from fine precision tubing to heavy-duty structural use.
With higher strength and uniformity, cold-drawn seamless steel pipes are widely preferred for hydraulic cylinders, mechanical parts, and high-pressure piping systems.
While CDS pipes are well-known for their accuracy and strength, they aren't perfect for every situation. Just like any material, they come with some trade-offs that buyers need to consider before placing bulk orders.
The cold drawing process requires multiple stages of processing, precision tooling, and additional labor. This makes the pipe more expensive compared to hot-rolled or welded pipes. For projects with tight budgets, this cost factor can be a challenge.
Since the cold drawing process is better suited for smaller diameters and thinner walls, it's harder to produce very large-diameter pipes using this method. For heavy infrastructure projects that require thick, wide pipes, hot-rolled seamless options may be more practical.
Because of the precision involved, production cycles for CDS pipes are often longer. If a project needs urgent delivery or bulk supply on short notice, this can cause delays.
Cold working increases hardness and strength, but it can also introduce residual stress into the steel. Without proper heat treatment, this stress may cause the pipe to warp, crack, or lose toughness under certain conditions.
The additional drawing and finishing steps require more energy compared to hot rolling. This not only impacts cost but also increases the environmental footprint of production.
The manufacturing of cold-drawn seamless (CDS) pipes is a multi-stage process designed to improve accuracy, strength, and surface quality. It starts with a hot-rolled seamless tube (often called a "mother tube") and then undergoes cold drawing at room temperature to refine its dimensions and properties.
Here's a simplified breakdown of the process:
Cold-drawn seamless (CDS) pipes are not just about strength and precision — they're about reliability in demanding environments. Because of their smooth surface, tight tolerances, and superior mechanical properties, these pipes are widely used in industries where performance, safety, and accuracy cannot be compromised.
| Industry | Typical Applications | Why Use Cold-Drawn Seamless Pipe |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Axles, steering columns, shock absorber cylinders, fuel injection systems | High dimensional accuracy and ability to withstand dynamic loads |
| Oil & Gas | High-pressure pipelines, drilling tubes, casing, offshore platforms | No weld seams → safer under extreme pressure and corrosive environments |
| Power Generation | Boiler tubes, heat exchangers, nuclear reactor tubing | Excellent heat resistance, pressure tolerance, and long service life |
| Hydraulic & Pneumatic | Hydraulic cylinders, actuator tubes, pneumatic system pipes | Smooth internal finish ensures efficient fluid flow and reduces friction |
| Mechanical Engineering | Shafts, bearings, precision-machined parts | Stable dimensions and good machinability |
| Construction | Structural supports, scaffolding, bridges, high-rise frameworks | High load-bearing capacity and structural reliability |
| Aerospace & Defense | Aircraft hydraulic systems, landing gear, missile casings | High strength-to-weight ratio, superior reliability under critical conditions |
CDS pipes are available in a wide range of sizes, wall thicknesses, grades, and standards. Below is a summary table to help buyers quickly understand typical specifications.
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Outer Diameter (OD) | 6 mm – 273 mm (can be customized) |
| Wall Thickness (WT) | 1 mm – 30 mm |
| Length | 3 m – 12 m (standard); cut-to-length available |
| Steel Grades | ASTM A179, ASTM A210, ASTM A213, ASTM A106, DIN 17175, EN 10305, etc. |
| Standards | ASTM, DIN, EN, JIS, GB/T |
| Surface Condition | Bright, annealed, pickled, phosphated, oiled |
| Tolerances | OD ±0.1–0.5 mm, WT ±10% (depending on size and grade) |
| End Types | Plain end, beveled end, threaded & coupled |
| Testing Methods | Hydrostatic test, ultrasonic inspection, eddy current, dimensional check |
| Heat Treatment Options | Normalizing, stress relieving, annealing |
| Delivery Form | Straight lengths or coils (for small-diameter tubes) |
Cold drawing and cold rolling are both finishing processes applied to steel pipes, but they are not the same. The main difference lies in how the steel is processed and the applications they serve.
Here's a side-by-side comparison for clarity:
| Aspect | Cold-Drawn Pipe (CDS) | Cold-Rolled Pipe |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Hot-rolled seamless tube is pulled through a die (with or without a mandrel) at room temperature | Pipe is reduced in diameter and wall thickness by passing through cold rolling mills |
| Dimensional Accuracy | Very high (tight tolerances in OD, ID, and wall thickness) | High, but generally less precise than cold drawing |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, bright, and uniform (inside and outside) | Improved surface over hot-rolled, but not as smooth as cold-drawn |
| Strength & Properties | Higher tensile strength, hardness, and toughness | Improved mechanical properties but lower strength than CDS |
| Size Range | Best for small to medium diameters and thin to medium walls | Better for larger diameter pipes with uniform thickness |
| Applications | Automotive parts, hydraulic cylinders, precision engineering, boilers | Structural applications, medium-pressure pipelines, construction |
| Cost | Higher (due to more processing steps) | Moderate (less complex process compared to CDS) |
Cold-drawn and hot-rolled pipes differ mainly in their manufacturing temperature, surface finish, and mechanical properties. Hot rolling happens at high temperatures, while cold drawing is performed at room temperature to refine the product further.
Here's a side-by-side comparison:
| Aspect | Cold-Drawn Pipe (CDS) | Hot-Rolled Pipe (HRS) |
|---|---|---|
| Processing Temperature | Drawn at room temperature (after initial hot rolling) | Rolled at high temperature (above recrystallization point) |
| Dimensional Accuracy | Very high (tight tolerances on OD, ID, and wall thickness) | Lower accuracy; may require machining for precision |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, bright, uniform (suitable for precision use) | Rougher, oxidized surface with scale |
| Mechanical Properties | Higher strength, hardness, and toughness due to work hardening | Softer, more ductile, easier to form and machine |
| Size Range | Typically small to medium diameters, thin to medium walls | Suitable for larger diameters and thicker walls |
| Applications | Automotive, hydraulic systems, boilers, aerospace, precision components | Pipelines, structural uses, construction, general engineering |
| Cost | Higher (more processing steps and tighter quality control) | Lower (simpler and faster production process) |
Cold-drawn seamless pipes are highly valued for their precision, smooth surface, and strength, but the cold-drawing process introduces residual stresses inside the steel. These stresses mainly come from uneven heating and cooling during manufacturing.
When the pipe cools after drawing or heat treatment:
Additionally, during heat treatment:
The magnitude of these stresses depends on several factors: cooling rate, steel composition, and pipe geometry. For example:
At Dexin, founded in 2002, we have been a trusted manufacturer and supplier of seamless steel pipes for over two decades. Our cold-drawn seamless pipes combine precision, strength, and reliability, making them the preferred choice for industries that demand high-quality, durable, and dimensionally accurate steel solutions.
Partnering with Dexin means choosing a supplier who understands your industrial challenges and provides tailored solutions that save costs, reduce maintenance, and guarantee reliable results. Experience the Dexin difference—where quality, expertise, and trust come together in every seamless steel pipe we deliver.
Complete Guide to Cold-Drawn Seamless Tubes | Anand Seamless
Cold Drawn Pipe Process: What Is It? - Precise
What is cold drawn seamless steel pipe?
Why do Cold Drawn Seamless Tubes need Heat Treatment?
Precautions for cold drawn precision seamless steel pipes
Your Name*
Your Email*